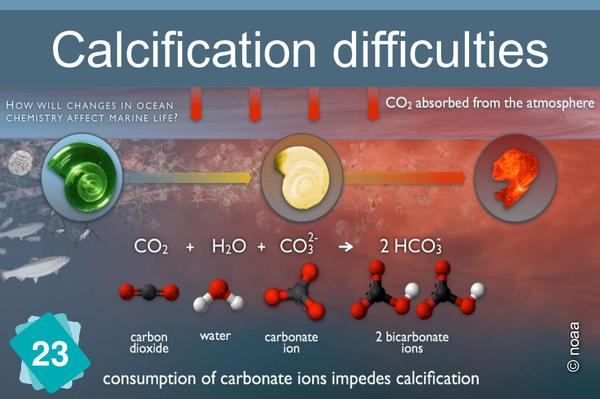
23 - Hindered calcification process
✏️ This explanation does not yet exist in your language. Please fill this Google Form if you want to help us!
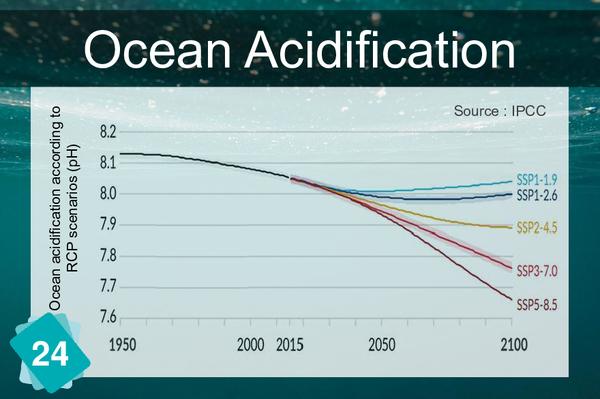
The formation of limestone (calcification) follows the chemical reaction Ca++ + 2HCO3- ⇔ CaCO3 + H2O + CO2. It requires the presence of bicarbonate ions (HCO3-). However, the quantity of these ions in water depends on the pH: in water, carbon dioxide, carbonic acid, bicarbonate ions and carbonate ions are in equilibrium, depending on the pH : CO2 + H2O ⇔ H2CO3 ⇔ H+ + HCO3- ⇔ 2 H+ + CO32-. The addition of an acid shifts the equilibrium towards the left of the equation. In other words, if the pH drops, there are fewer bicarbonate ions, making it more difficult for organisms to build their shells.